In the medical field, and particularly in the dental sector, diagnosis is one of the most important phases of therapy. For endodontic treatments, for example, the pulp vitality test is essential for planning a specific cure.
Endodontic therapy
Endodontics is that sector of dentistry that deals with the morphology, physiology and pathology of dental pulp, as defined by the American Association of Endodontists, in its “Quality Assurance Guidelines” published in 1987.
Endodontic treatment consists of three phases:
- diagnosis;
- preparatory phase: cleansing and cleaning of the infected area;
- seal of the affected area.
The three phases are closely related to each other, the more accurate and precise the diagnostic phase, the greater the probability of success of the therapy.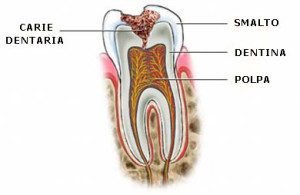
Clinical tests
The pulp vitality represents the state of health of the tooth pulp and serves to establish whether the tooth is still “alive”. Sometimes the objective examination and the patient’s clinical history alone are not sufficient to establish the state of the pulpo-dentin system.
There are specific clinical tests to measure pulpal vitality, useful parameters to understand which treatments to carry out and what possible contraindications there could be.
An accurate diagnosis consists of an extraoral assessment, an analysis of the oral cavity and specific clinical tests.
Extraoral clinical examination
The extraoral clinical examination involves the evaluation with respect to symptoms present outside the oral cavity:
- swelling;
- facial asymmetries;
- pain;
- swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
Intraoral examination
The examination of the oral cavity foresees the overall evaluation of the mouth:
- presence of mucosal lesions;
- gum swelling;
- presence of caries or infections;
- presence of fractures or microfractures.
Pulp vitality test
Clinical tests for the examination of pulp vitality are the specific part relating to the state of the tooth pulp. The test can be performed in various ways described below.
Test with thermal stimuli: cold
To perform the test with cold stimulus, ethyl chloride is used in the liquid state, a substance which, when vaporized, reaches temperatures between -10 ° and -25 °. The tooth to be examined is treated with a cotton swab dipped in ethyl chloride and the patient’s reaction is evaluated based on thermal sensitivity. The test is performed in a comparative manner, the same operation repeated on a healthy tooth determines the actual hypersensitivity of the diseased tooth.
Test with thermal stimuli: warm
This test is also based on a thermal stimulus and a comparative system. For the test, warm gutta percha is used, in a healthy tooth there is only the sensation of heat that vanishes when the source is removed. If the tooth is affected by pulpitis the pain can be very strong and persistent, even after the heat source has been removed.
Test with electrical stimuli
This type of test cannot be performed on patients with pacemakers, in fact it is based on the transmission of electric current towards the pulp of the tooth to verify its vitality. In the absence of pain the pulp vitality is absent, therefore the tooth could be necrotic and therefore “dead”.
The tests listed above could still be distorted by the patient’s subjective responses to different stimuli. Based on stimuli and comparative perception it could happen that the patient does not clearly show the pain. There are therefore other texts that are based on the detection of the blood flow inside the pulp, useful for assessing with certainty the pulp vitality.
Laser-Doppler flowmetry test
The test consists in using a laser beam towards the tooth, the ray deviates when the light beam collides with red blood cells, in this way the pulp vitality is determined through the blood flow of the pulp.
Pulse oximetry test
With this test instead the hemoglobin is measured and therefore the quantity of oxygen present, useful for determining the vitality of the pulp of the tooth.
These clinical tests therefore disregard the patient’s perception and response, and are therefore considered more reliable, even if the traditional cold thermal stimulus test retains its validity and is considered the most reliable of the classic tests.