Also known as pyorrhea, periodontitis is a disease that affects the gums. Going more specifically, it is actually an infection that affects all the tissues that support the teeth such as the gums, alveolar bone, tooth root cementum and the periodontal ligament. Periodontitis has always been a pathology that has created various inconveniences, but what is often not underlined is that it is possible to cure it.
But, in the meantime, what can you eat and what should you avoid to limit it?
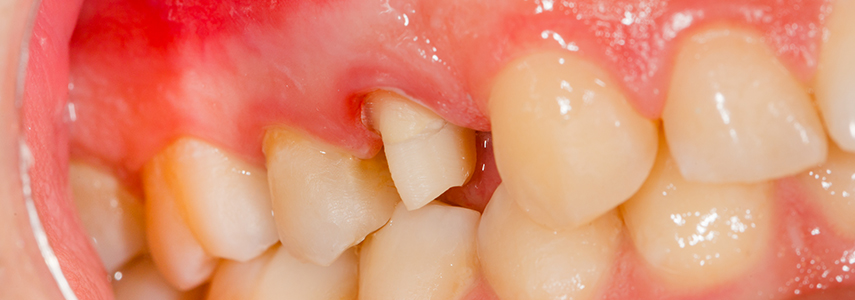
What is periodontitis and how to recognize it
Periodontitis has now become a very common disease, but fortunately preventable. When the gums bleed and retreat, they are not always taken as a warning sign or as symptoms of a disease. Neglecting these small inconveniences is never a good idea and action should be taken immediately. To do this, however, we need to carefully pay attention to our mouth and contact a periodontist in time to be able to prevent the inflammation from getting worse and causing a progressive worsening of the gingival and bone structure. So how do you know if it’s actually periodontitis? How to recognize it? What are the symptoms? Here are the most common ones that should never leave you indifferent:
- Inflamed and painful gums;
- Teeth moving;
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss your teeth
- Gum recessions;
- Increased space between the teeth;
- Halitosis;
- Periodontal abscesses and pus between the teeth.
Causes of periodontitis and why it is underestimated

Periodontitis is a pathology that is too often underestimated and this gives it an easy life insinuating itself between the teeth and worsening our oral health. According to research by the World Health Organization, periodontal problems are undermining the quality of life of Italians who, in the worst cases, risk being left without teeth. According to this study, in fact, as many as 20 million Italians over 35 are affected by this problem, as many as 8 who suffer seriously from it. Among these, unfortunately, only a few know the symptoms, the consequences and know they have it. Again according to this research, in fact, 70% of Italians have confused ideas on the subject of periodontitis. There are essentially two main causes of this pathology: bacteria and heredity.
Every day when we eat, a platoon of bacteria energetically lashes out against our teeth. By washing them immediately after meals, we can protect them from the 100,000 microorganisms that are the cause of tooth decay and gum inflammation. However, 4 hours after a meal, if you don’t brush your teeth, these microorganisms multiply into millions, creating a layer on your teeth that can facilitate infections.
This is where gingivitis originates which can worsen turning into periodontitis (or pyorrhoea). On the other hand, when we talk about the hereditary nature of this disease, we mean the fact that this pathology affects in particular the most genetically exposed people, i.e. those who have a family history of periodontitis. These subjects should pay more care and attention to their teeth than others, through constant, careful and correct oral hygiene and specific dental habits. If you are more at risk of pyorrhea, for example, you should be careful how you brush your teeth, but especially what to eat and what would be better to avoid. In the next paragraph we will go into specifics about this, making a list of foods that are friends and enemies of the teeth for periodontal subjects.
Gum problems, what to eat and what to avoid

Preventing periodontitis with proper nutrition is increasingly proving to be an extremely effective solution. It becomes possible to do so because there are foods capable of relieving the symptoms of pyorrhea. There are also some foods that are defined as “friends of the teeth”. Among these, the ones most recommended to do so are first of all fruits and vegetables with a high content of vitamin C and antioxidants. Citrus fruits such as oranges and lemons are especially recommended, whose antiseptic function facilitates the healing process in case of inflammation. Citrus fruits have the ability to heal and tone bleeding, inflamed and/or irritated gums. Similarly, kiwifruit and other foods rich in vitamin E can also stop gum bleeding.
In addition to fruit, as we have said, excellent foods capable of anesthetizing inflamed or bleeding gums are vegetables and greens, especially if eaten raw. Among them, it is better to favor onions, which possess some of the strongest antibacterial properties. A study shows that if the onion is eaten raw it is able to break down at least four bacterial strains on the gums. It is also an excellent idea to take yogurt with live lactic ferments or a probiotic in case of prolonged antibiotic therapy (to strengthen the immune system). Then there are shiitake mushrooms, even if they are not well known, they can help as they contain important elements such as lentinan (a natural sugar that has a preventive action). On the other hand, there are foods to avoid if you have pyorrhea, to which we must add the absolute contraindication of tobacco. It is mainly about:
- Fried;
- Fatty foods;
- Crunchy foods;
- Alcohol;
- Milk and derivatives immediately after the administration of antibiotics;
- Jam, honey, chocolate, caramel and other sticky foods;
- Foods and/or drinks rich in sugar.
Regardless of the right diet to follow or some precautions that we have listed that can relieve inflammation, the safest remedy to limit or eliminate periodontitis is to consult a specialist. In our Sanident center in Milan, in via Settembrini 6, you will find all the information you need to fight your gum problems. Book a first visit without obligation now and find out how to improve the quality of your life.