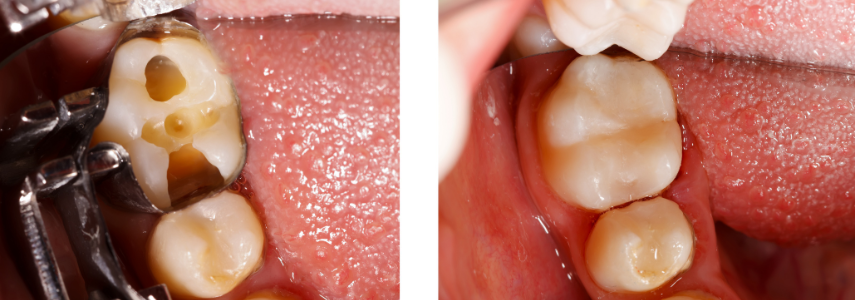
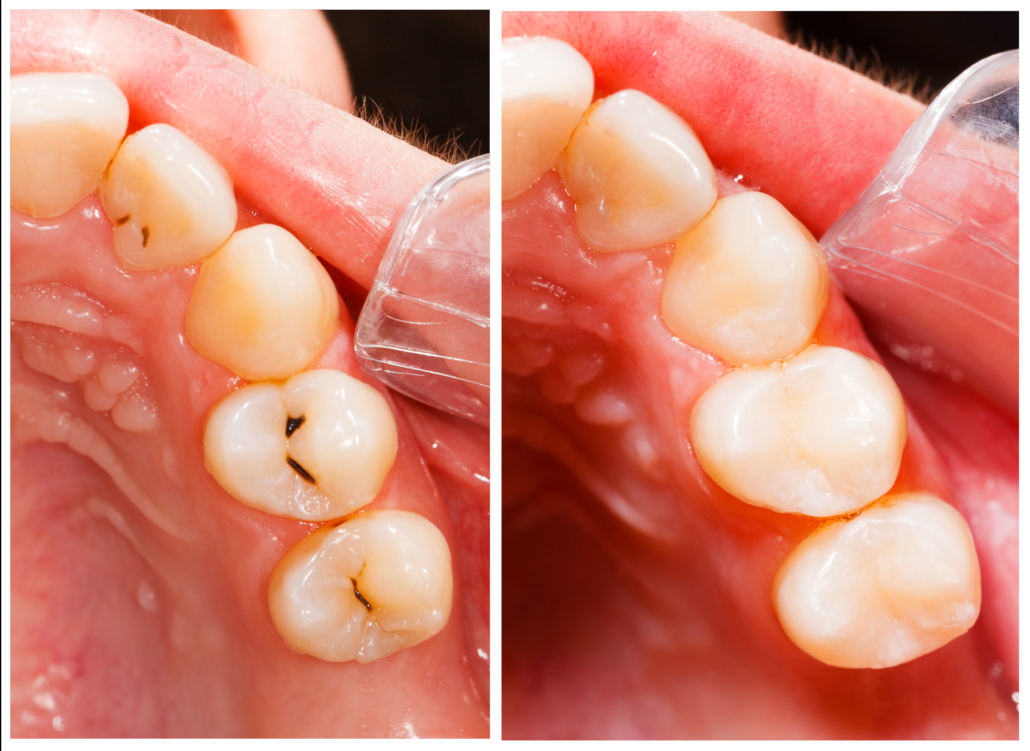
Many patients ask for a dentist appointment to recover damaged restorations. The main interventions for which you “put your hand back” on a previously restored tooth are: recurring caries, wear, discoloration, loss of material.
Repair the restorations or replace them?
Completely replacing previously treated restorations can cause complications for the patient. In fact, irritation of the pulp of the tooth or the removal of healthy parts of the tooth itself can occur. It is also necessary to consider that this type of intervention is also very invasive for the patient.
Therefore, on damaged restorations, alternative and less invasive treatments can be proposed to the patient:
- repair of restorations;
- edge sealing;
- restoration of the restoration.
Repairing a damaged restoration versus its complete replacement has multiple benefits for the patient:
- anesthesia is not necessary;
- few sessions are needed;
- the costs are contained.
Repairing damaged restorations – is it always feasible?
In a study, published in JADA in November 2021, researchers evaluated the main variables of repair of damaged restorations versus replacement.
A 15-question questionnaire was administered to American Dental Association member dentists over a two-week period in 2019. Descriptive, bivariate and multivariate analyzes were conducted.
Of the 387 dentists interviewed, 83.7% said they repair defective restorations and 16% said they always replace them.
The reasons that led the dentists interviewed to give up repairing the restoration were:
- the size of the defect and the extent of the carious lesion (42%);
- previous negative experiences (37.9%).
The frequency of choosing to repair damaged restorations instead of completely redoing them was higher. In fact, negative personal experience or treatment failure related to past cases influences dentists on the decision to repair or replace a damaged restoration.
In any case, the dentist will evaluate the type of treatment based on the specific clinical conditions of each patient, only in this way can the most appropriate treatment be guaranteed for the individual clinical case.