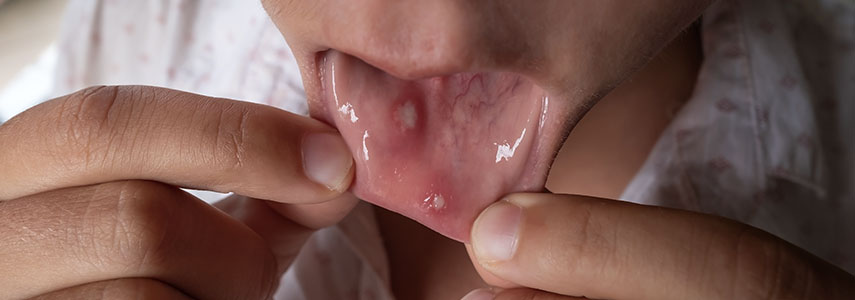
Oral stomatitis or mucositis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. It is a disease that can lead to mild disorders or degenerating into a disabling disease.
The causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory process whose origin is not yet clear, but it is certainly influenced by some factors, in particular, the main causes of mucosal inflammation are: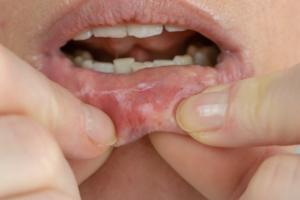
- anticancer therapies;
- nutritional deficiencies;
- poor oral hygiene;
- smoking habit;
- genetic predisposition.
It is very likely that cancer patients subjected to anticancer therapies, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, they develop oral mucositis, due to the fragility of oropharyngeal tissues.
Symptoms of oral mucositis
Stomatitis presents with a gradual symptomatology. The first symptoms may also be mild, such as redness of the mucosa. Then you may experience a burning sensation.
The progression of the pathology leads to more painful consequences for the patient, there are cases in which stomatitis can become a debilitating disease, also due to the difficulty in eating.
The aggravation of oral mucositis involves:
- dry mouth;
- soft tissue edema;
- ulcerations;
- acute pain;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing;
- gum bleeding;
- dentinal hypersensitivity;
- loss of voice.
Intervening in a timely manner on inflammation avoids health complications.
In addition, stomatitis can extend from the oral cavity to the upper airways and to the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment of oral mucositis
As with other oral cavity diseases, prevention is always the best cure. Maintaining a correct and constant oral hygiene, brushing the teeth after each meal, significantly reduces the risk of any infection.
Added to this is the correction of bad habits that can increase the risk of stomatitis, including:
- stop smoking;
- avoid abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- avoid foods that are too hot or too spicy;
- avoid dehydration of oral mucosa by drinking plenty of water.
From the point of view of dental treatments, to reduce pain, the dentist could prescribe rinses with solutions that have an anti-inflammatory component.
In more serious cases it is prescribed the application of a gel inside the oral cavity which can act as a protective film for the mucous membranes and which, at the same time, is curative for small lesions and analgesic for persistent pain.
When stomatitis is due to oncological therapies such as radiotherapy or chemotherapy, the dentist may prescribe systemic analgesic therapy based on paracetamol or anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In these cases, therapy may be necessary for longer periods to reduce discomfort and pain.