Nocturnal bruxism in children is a phenomenon in sharp increase, it is a dental and gnathological pathology characterized by the involuntary movement of the jaw and the grinding and clenching of the teeth.
Types of bruxism
Bruxism is divided into two different types:
- sleep bruxism, precisely nocturnal bruxism;
- daytime bruxism, which occurs during the waking state.
Nocturnal bruxism can be the cause of damage, of various degrees, to the stomatognathic system, including:
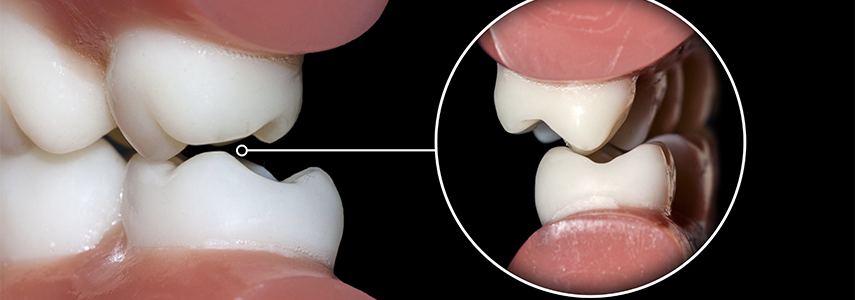
- tooth wear;
- pain in the jaw;
- pain in the temporomandibular joint;
- periodontal trauma.
Night bruxism in children: pathology on the rise
Night bruxism in children and adolescents has an incidence ranging from 3 to 49%.
The repercussions on the health of children suffering from nocturnal bruxism can be manifold:
- repercussions on behavior and cognitive functioning;
- decreased quality of sleep;
- tiredness;
- increased cortisol levels.
Some scientific studies show that children who do not like to play sports are more prone to sleep disturbances, anxiety, stress, cognitive disorders and unhealthy habits such as nail biting and biting objects.
Sleep disturbances and nocturnal bruxism in children
Recent research published in the scientific journal Oral Disease of May 2021, dentists and psychologists have investigated the association between sleep disorders and probable bruxism in children between eight and ten years of age.
From the analysis of the sample taken into consideration for the research, it emerged that nocturnal bruxism was present in 9.1% of 58.6% of children with sleep disorders.
From the socio-demographic questionnaire to which the parents of the children involved in the analysis responded, it also emerged that bruxism in children was also associated:
- family instability;
- do not play sports;
- have sleep-wake transition disturbances;
- being sleepy for excessive daylight hours.
Preventing Bruxism in Children
As with other dental pathologies, bruxism in children can be prevented thanks to the synergy of several medical skills. The collaboration between dentist, pediatrician, psychologist can help to sensitize families about sleep disorders and the likelihood of developing bruxism.
If diagnosed in time, all the dental and gnathological consequences of bruxism such as wear of the teeth, posture and speech problems can be avoided.