Interproximal enamel reduction is a dental treatment that allows the reduction of tooth width by controlled abrasion of excess enamel in the interproximal area of the teeth.
When is interproximal enamel reduction necessary?
Interproximal enamel reduction, also called enamel stripping, is a dental technique that is used when light dental crowding occurs. In fact, through stripping the excess enamel part is eliminated, a minimum quantity that can vary from 0.5 mm to 0.8 mm, without affecting in any way the natural structure of the tooth.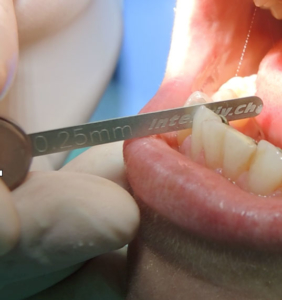
By applying this dental technique to the interproximal areas of the teeth it is possible to create more space in the arch, recovering between 4 and 6 millimeters overall.
It is possible to opt for the interproximal enamel reduction in several cases, however these are very mild clinical situations:
- dental crowding;
- orthodontic support;
- dento-alveolar discrepancy;
- teeth too close together.
Not all patients have such a clinical condition that they can face enamel reduction; although it is a technique that can be performed safely, there are still some contraindications.
Patients who presented the following issues:
- worn and thin enamel;
- presence of removable prostheses or dental implants;
- malocclusion;
they may not be in a position to take an interproximal enamel reduction treatment.
How is interproximal enamel reduction performed?
The first step in stripping dental enamel is a diagnostic imaging exam. Image acquisition  digital and three-dimensional allows the dentist to evaluate which teeth can be used to reduce the enamel.
digital and three-dimensional allows the dentist to evaluate which teeth can be used to reduce the enamel.
Being a dental therapy that includes a millimetric intervention field, the use of the surgical microscope allows to perform the action with the maximum precision.
The tools used for stripping the enamel can be mechanical or manual: the teeth are separated from each other by special instruments and then proceed with controlled abrasion of the enamel.
In the final phase of the treatment the enamel is finished.
Post intervention
Interproximal enamel reduction does not give rise to particular contraindications. One of the consequences that could occur in the immediate post-surgery is a slight hypersensitivity of the teeth and a demineralization of the enamel.
To overcome this problem, a fluoride-based therapy is often recommended, in order to re-mineralise the enamel. To this indication is added that of having greater care in daily oral hygiene, especially in the days following the treatment. Hypomineralization of the enamel could expose the tooth to plaque attack, causing infections or tooth decay.
Tips
Interproximal enamel reduction is a highly accurate dental technique, so the small annoyances that result should last a couple of days at most. To be carried out in the best way, experience and good technical manual skills are required, as well as a millimetric planning of each action. Relying on expert hands is the only guarantee of success.
















