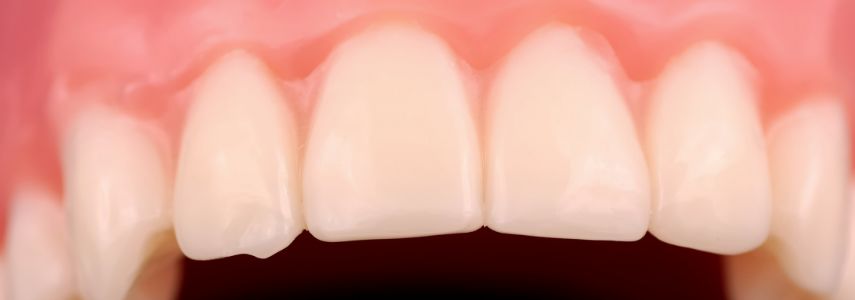
Gingivitis is nothing more than inflammation of the gums, it is a very common pathology and is mainly manifested by the redness, bleeding and swelling of the gums themselves.
In its initial phase, gingivitis is not painful, for this reason it is often overlooked. The first symptoms, including bleeding gums during tooth brushing, are confused with temporary discomforts. Not intervening promptly on an incipient gingivitis could cause serious damage to the health of the mouth.
The causes of gingivitis
The main cause of gingivitis is plaque buildup. The bacteria that nestle between the tooth and the gum, in what is defined as the gingival sulcus, give rise to inflammation.
If stimulated, the gums begin to swell and bleed because during the bacterial attack they are mostly sprayed with blood, a means by which the body makes the antibodies reach the area affected by the infection.
24 hours without proper oral hygiene are enough to trigger a bacterial attack in the vicinity of food residues stuck between the teeth.
The inflamed gums thus begin to lose their adhesion to the tooth because the plaque creates serious damage to the fibroblasts, the cells responsible for the compactness of the tissues.
What happens if gingivitis is not treated
 Gingivitis is a pathology that should be addressed promptly, the more time passes, in fact, the more the inflammation degenerates with the possibility that it turns into a periodontitis. The transition between a reversible infection and an irreversible inflammatory pathology is not so long, in fact periodontitis can irremediably lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis is a pathology that should be addressed promptly, the more time passes, in fact, the more the inflammation degenerates with the possibility that it turns into a periodontitis. The transition between a reversible infection and an irreversible inflammatory pathology is not so long, in fact periodontitis can irremediably lead to tooth loss.
If the plaque is not removed, the inflammation tends to worsen, the gums retract and the tooth collar remains exposed. The periodontal pockets, loaded with bacteria, become deeper and deeper until they reach the periodontal ligament and the maxillary bone.
This is the point of no return. The moment when gingivitis turns into periodontitis. The gingiva begins to detach from the tooth, the gingival sulcus widens and the treatments become more and more complex until it becomes impossible to save the teeth.
When the pathology is about to reach this stage, the symptoms will be evident and unequivocal:
- Swollen and red gums
- Even spontaneous bleeding
- Pain when chewing
- Halitosis
- Hypersensitivity of the teeth
A hormonal imbalance could also facilitate the onset of gingivitis, which is why pregnant women are particularly subject to the possibility of incurring inflammation of the gums.
Gingivitis treatment
Gingivitis is cured by removing the cause of its origin. For this reason, it is possible to heal gingivitis through the deep cleaning of plaque and tartar with a professional scaling treatment performed by the dentist.
The scaling performed at least twice a year is the best therapy also for the prevention of gingivitis to which it would be appropriate to add the following daily indications:
- brush your teeth for at least two minutes after each meal
- in the case of red gums, use a soft bristle brush to avoid worsening inflammation
- regularly use dental floss to thoroughly clean the oral cavity of food residues
- use a mouthwash also indicated for the disinfection of the gums
They are small precautions that take away only a few more minutes during the day, but which over time can bring enormous benefits to the health of the mouth and the general well-being of the organism.