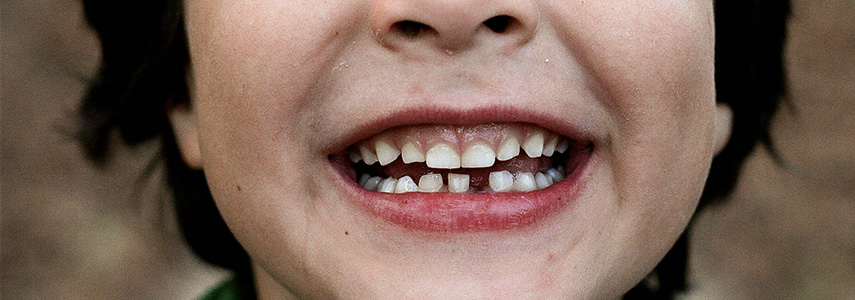
The ankylosis of the deciduous tooth is a rather rare pathology, it is characterized by the impossibility of tooth eruption due to an abnormal fusion between the root of the tooth and the bone.
How does ankylosis of the tooth occur?
With the term ankylosis, the lack of possibility of the tooth to move and correctly perform the process of eruption from the maxillary bone is indicated in the medical field. This can also occur due to the absence of the periodontal ligament.
The ankylosis of the tooth can affect both deciduous and permanent dentition. The causes of tooth ankylosis can be genetic or hereditary or they can be the consequence of other types of pathologies involving atrophy of the cells of the periodontium.
Atrophy of the periodontal ligament cells can occur following:
- abnormalities in bone development;
- alterazioni del metabolismo;
- infections;
- lack of development of tooth tissues;
- traumatic events.
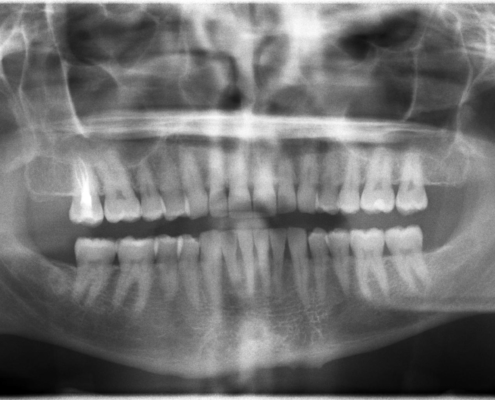
The symptomatology of dental ankylosis involves a difficulty in chewing and the presence, visible even to the naked eye, of the tooth incorporated in the bone. The tooth may be completely submerged or only a small part of it may emerge.
The most frequent symptoms are:
- temporomandibular joint pain;
- malocclusion;
- headache.
The certainty of the diagnosis can be obtained by the dentist using imaging diagnostic tools.
How to intervene in cases of ankylosis of the tooth
In the event of ankylosis, the dentist will be able to evaluate the type of dental treatment to follow based on the patient’s age and the complexity of the specific clinical case.
Partial ankylosis of the tooth
In cases in which the ankylosis of the tooth is partial, one usually proceeds with subluxation-dislocation of the tooth and then proceed with an orthodontic treatment that helps the dental element to find its right position in the dental arch.
Complex cases of ankylosis
Some clinical cases, related to ankylosis, can be treated exclusively with thetooth extraction ankylosed.
In pediatric patients, where the pathology concerns the deciduous teeth, the extraction of the tooth affected by ankylosis will allow the subsequent development of the permanent teeth which can be accompanied by an orthodontic treatment for the correct placement of the emerging tooth.
Ankylosis of the permanent tooth
When the ankylosed tooth is a permanent tooth, it is possible to opt for a complex surgical osteotomy aimed at repositioning the ankylosed tooth without sacrificing the dental element or, in the absence of alternatives, proceeding with tooth extraction.
Being a permanent dentition, the extracted tooth can be replaced with an implant operation when the patient has reached skeletal maturity, ie when jaw and mandible will have completed their development process.