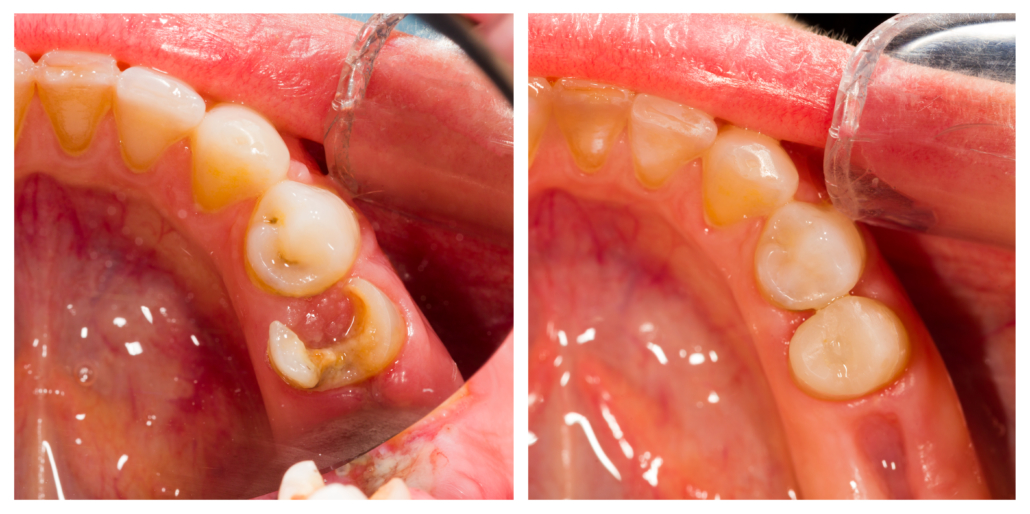
After root canal treatment, the teeth become much more vulnerable and are more exposed to biomechanical forces precisely due to the loss of the internal structure of the tooth after devitalization.
The decayed tooth is cleaned of the infected part and subsequently reconstructed, but the type of direct or indirect restoration can affect the future resistance of the tooth to masticatory forces.
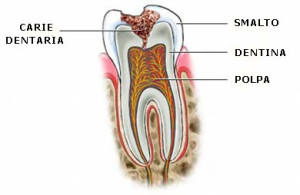
Direct or indirect restoration?
Given that there is never a standard solution to a dental problem, the dentist can evaluate the individual clinical case before proceeding with the most effective treatment for the individual patient.
Regarding the question of whether after root canal treatment it is more appropriate to perform a direct or indirect restoration a study has been published on Journal of Adhesive Dentistry in which, through a systemic review of the cases present in the scientific literature, the survival rates of direct and indirect restorations were evaluated.
From the analysis of the clinical cases taken into consideration, it emerged that a good part of dentists opt for tooth encapsulation after endodontic treatment.
Tooth encapsulation after root canal treatment does not always seem to be necessary, this is what research has shown.
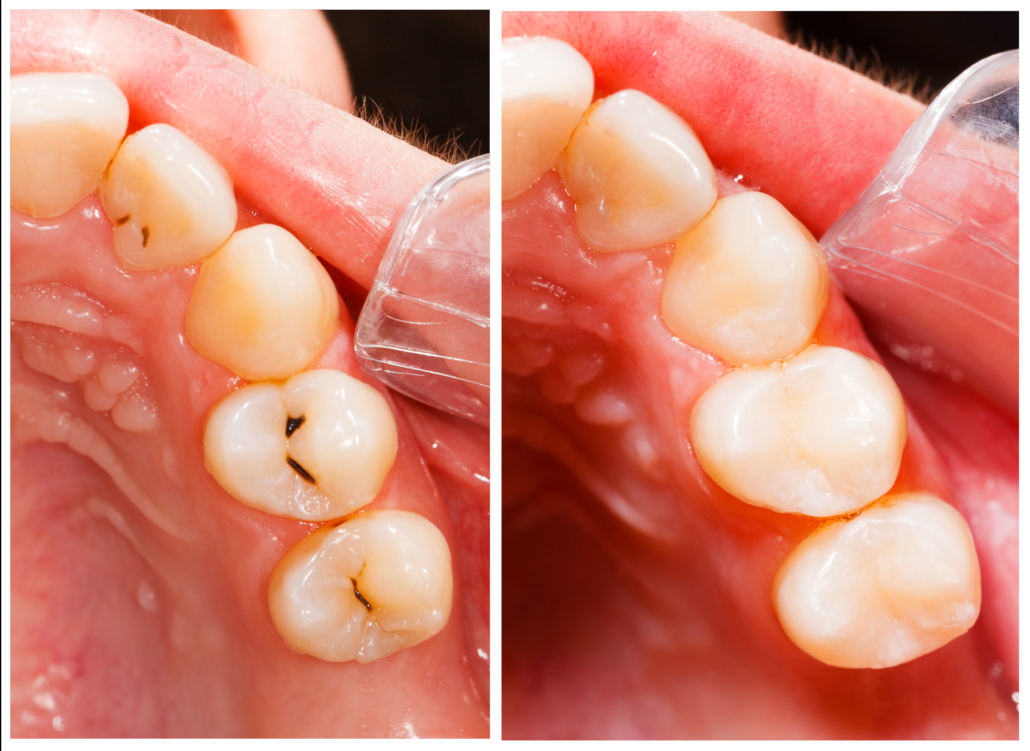
Main clinical indications after root canal treatment
Based on the data that emerged from the research, the researchers tried to systematize the main clinical indications that dentists could follow for restoration after tooth devitalization.
Direct restorations after root canal treatment
From what emerged from the information gathered on the clinical cases analyzed, direct composite restorations are an effective treatment for teeth that have suffered minimal loss of tooth structure during devitalization. Particularly with moderate loss of the tooth crown.
Indirect restorations after endodontic treatment
Indirect restorations, on the other hand, are more appropriate for teeth that have had significant damage to the crown following root canal treatment. In these cases, encapsulation is the best treatment to protect the tooth from the stress of chewing forces.
Resistance of the restorations
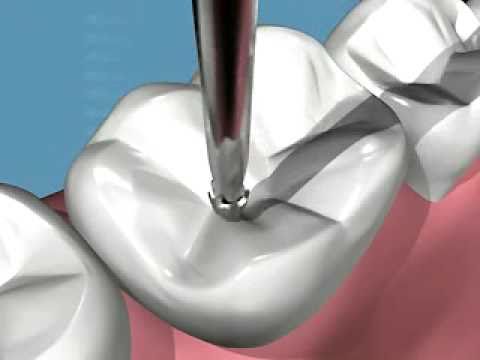
Compared to the success of endodontic treatment, both restoration modalities demonstrated a minimum survival of 5 years.
Indirect restorations are more durable in the long term (10 years) and have better performance in terms of aesthetics and functionality.
The opinion and evaluation of the dentist on the individual clinical case always remains of fundamental importance, the decision with respect to the type of restoration must be evaluated with respect to the quality of the tooth after root canal treatment and other specificities of the individual patient.