Localized aggressive periodontitis is a particular form of periodontitis which, as the definition itself suggests, specifically targets permanent incisors and first molars.
What distinguishes aggressive localized periodonitis from chronic periodontitis?
Localized periodontitis affects adolescents and young adults in particular, the very aggressive character of the pathology determines its rapid progression and it is difficult to reverse this progress in the acute phases of the disease.

Preventing the onset of aggressive periodontitis is the only way to intervene on the serious consequences that the progress of the pathology entails.
An important variable at the origin of localized periodontitis is hormonal changes. For example, in the passage from the deciduous to the permanent dentition, a variation of the microbial environment occurs. During the eruption of the first molars and permanent incisors, the variation of the oral microbiota could determine the onset of the disease.
Possibility of intervention and care
Some scientific studies published recently on JADA have tried to investigate the differences between localized aggressive periodontitis and chronic periodontitis. The research was also aimed at identifying different types of treatment of oral pathology.
The results of the research showed that the two types of periodontitis have different characteristics and in particular it has been highlighted that:
- localized aggressive periodontitis mainly affects first molars and incisors, while chronic periodontitis is not so specifically localized;
- aggressive periodontitis occurs in very young subjects and progresses faster than chronic periodontitis that affects adults and the elderly;
- the causes of chronic pyorrhea are due to the competition of many genetic factors, while for localized pyorrhea it is possible to trace a correlation only with the inheritance of relatives of a very close degree;
- the main bacteria responsible for localized aggressive periodontitis are Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and hyper-reactive neutrophils.
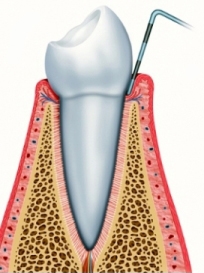
Early diagnosis and follow up
The research, as a whole, has highlighted how it is necessary to think of the two types of periodontitis as distinct pathologies, so it would be necessary to deepen separate scientific studies.
As regards treatment and cure, antibiotic and non-surgical therapies are envisaged for the aggressive localized periodontitis, considered to be the most effective at the moment.
However, it is not always possible to intervene in time with dental care, the disease often occurs without particular symptoms and progresses rapidly.
Early diagnosis is the most effective way to deal with aggressive periodontitis localized at the right times and with the possibility of avoiding serious consequences, such as tooth loss.